Function Authentication¶
With OpenFaaS Identity and Access Management (IAM) you can secure function endpoints without having to write any additional code. Access permissions for functions can be configured using IAM Roles and Policies.
Note
Function authentication is currently under technical preview
You can follow this comprehensive tutorial form our blog to get started with built-in function authentication: Introducing built-in authentication for OpenFaaS Functions
Enable built-in authentication¶
OpenFaaS Identity and Access Management needs to be enabled and configured in order to use function authentication, see: Identity and Access Management (IAM)
To enable function authentication your functions need to be using a compatible version of the OpenFaaS watchdog. For the classic-watchdog this is any version > 0.2.3. The of-watchdog support function authentication for releases > 0.9.15.
Authentication can be enabled on a per function basis by setting the jwt_auth environment variable to true in the function configuration, e.g:
functions:
figlet:
skip_build: true
image: ghcr.io/openfaas/figlet:latest
environment:
jwt_auth: true
Note
Existing functions using an older watchdog version and functions without the jwt_auth environment variable are not affected if you start using built-in function authentication. By default all functions can be invoked without authentication.
Define Roles and Policies¶
Create a new policy or update your existing policies and include the Function:Invoke action to allow function invocations.
The resource field can be used to specify what resources the Function:Invoke action is applied to:
*- allow invocations for all functions in the clusterstaging:*- allow invocations for all functions in a namespace. In this case thestagingnamespace.openfaas-fn:env- allow invocations for an individual function.
The following policy will allow the env function in the dev namespace to be invoked, and any function in the openfaas-fn namespace:
apiVersion: iam.openfaas.com/v1
kind: Policy
metadata:
name: invoke-policy
namespace: openfaas
spec:
statement:
- sid: 1-invoke-policy
action:
- "Function:Invoke"
effect: Allow
resource:
- "openfaas-fn:*"
- "dev:env"
Create a Role to map the invoke-policy to a user or group:
apiVersion: iam.openfaas.com/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: invoke-role
namespace: openfaas
spec:
policy:
- invoke-policy
condition:
principal:
jwt:sub:
- a9e0e67a-5758-4373-a4ba-23957fa66e6b
StringEqual:
jwt:iss: ["https://keycloak.example.com/realms/openfaas"]
Invoke authenticated functions¶
To invoke a function that has authentication enabled you need to obtain a function access token. Function access token can be obtained by exchanging a valid ID token or OpenFaaS API access token for a function access token through the OpenFaaS Gateways token exchange endpoint.
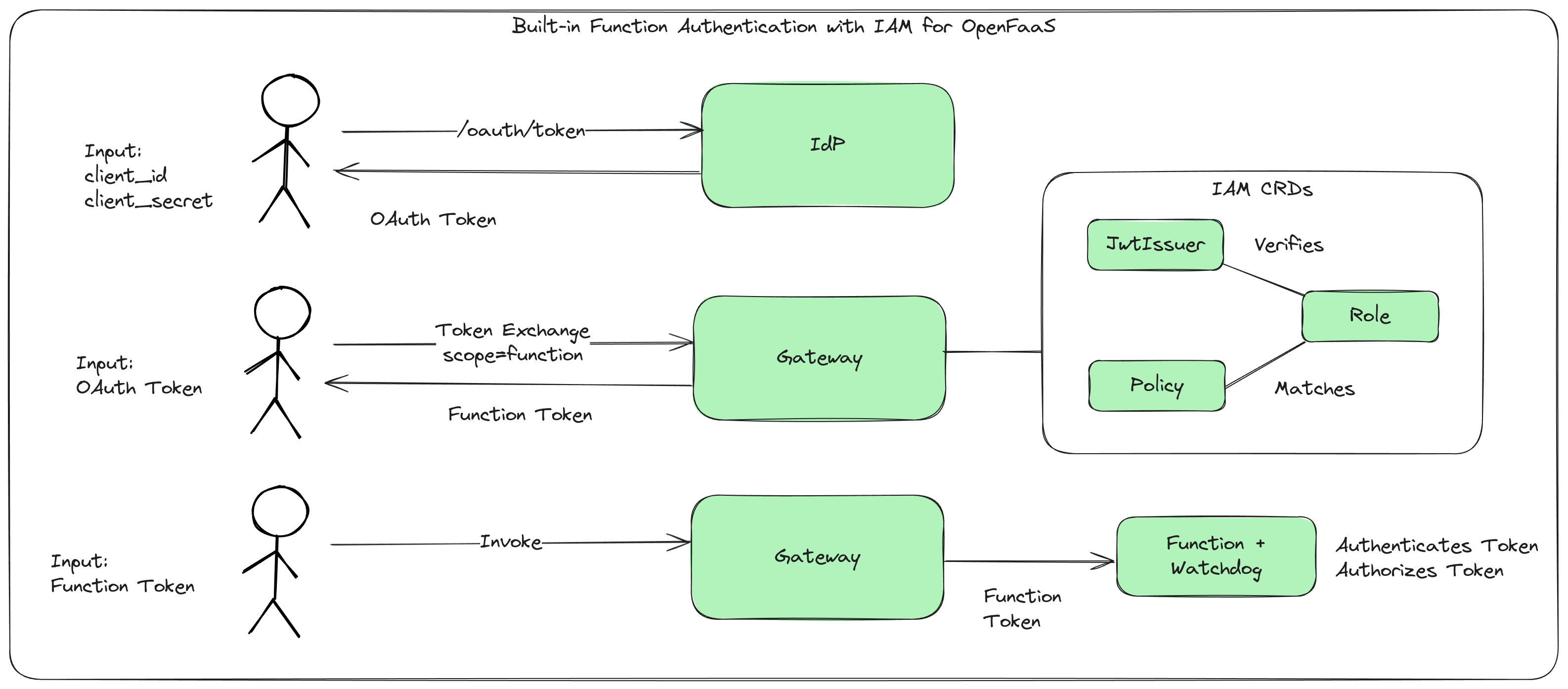
Function authentication flow from IdP to function invocation.
-
Obtain an OIDC ID token
Obtain an initial token that can be exchanged for a function access token. This can either be an OIDC ID token from an identity provider registered with OpenFaaS or an OpenFaaS API access token.
This example uses the OAuth2 client credentials flow. This flow can be used for machine to machine interactions and does not need human interaction. Any other OAuth flow or mechanism supported by your identity provider can be used to obtain the initial ID token.
export IDP_TOKEN_URL="https://keycloak.example.com/realms/openfaas/protocol/openid-connect/token" export CLIENT_ID="openfaas" export CLIENT_SECRET="$(cat ./client-secret.txt)" curl -S -L -X POST "${IDP_TOKEN_URL}" \ --header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ --data-urlencode "client_id=${CLIENT_ID}" \ --data-urlencode "client_secret=${CLIENT_SECRET}" \ --data-urlencode 'scope=email' \ --data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials' -
Exchange a token for a function access token
Call the token exchange endpoint to exchange the ID token or OpenFaaS API access token obtained in step 1 for a function access token.
Permission attenuation
The optional
audienceparameter can be used to reduce the permissions of a function access token so that it can only be used to invoke a single function, or a subset of functions.export IDP_TOKEN_URL="https://gateway.example.com/oauth/token" export TOKEN="$(cat token.txt)" curl -S -L -X POST "${IDP_TOKEN_URL}" \ --header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ --data-urlencode "subject_token=${TOKEN}" \ --data-urlencode "subject_token_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type:id_token" \ --data-urlencode 'grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:token-exchange' \ --data-urlencode 'scope=function' \ --data-urlencode 'audience=openfaas-fn:env' # Optional audience parameter -
Invoke an authenticated function
Invoke an authenticated function with the function access token.
curl -i "https://gateway.example.com/function/env" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $(cat ./function-token.txt)"
Invoke authenticated functions with the faas-cli¶
The faas-cli invoke command can be used to invoke authenticated functions. You will only be able to invoke authenticated functions if the CLI is authenticated with the gateway, faas-cli pro auth.
echo "OpenFaaS" | faas-cli invoke figlet
For more info on using the CLI with IAM for OpenFaaS, see: SSO with CLI
Auto-detection for authenticated functions
The CLI detects if a function needs authentication by calling the function a first time without any authorization header. If it receives a 401 response code the response is inspected to check if authentication with a function access token is required. If this is the case the CLI automatically retries the request with an access token.
If you know that a function needs authentication you can provide the optional --auth flag to skip the detection step. The CLI will immediately include the access token in the first call.