Overview
Identity and Access Management (IAM)¶
OpenFaaS for Enterprises includes a built-in Identity and Access Management (IAM) system that can be used to control access to the OpenFaaS REST API.
- Enable least privilege access to functions and secrets
- Use short-lived tokens for all API operations
- Enable Single Sign-On for all your users
- Deploy from CI/CD systems without long-lived shared secrets
- Audit all operations performed through the OpenFaaS REST API
Installation¶
We recommend you to follow this comprehensive walkthrough blog post to get started with OpenFaaS IAM: Walkthrough of Identity and Access Management (IAM) for OpenFaaS.
IAM can be enabled through the OpenFaaS Helm chart:
iam:
enabled: true
systemIssuer:
url: https://gateway.openfaas.example.com
The parameter iam.systemIssuer.url is the public url the gateway is accessible at. See Configure Ingress to setup ingress for the OpenFaaS gateway.
Next steps:
- Configure your identity provider and register it with OpenFaaS
- Configure SSO for the OpenFaaS dashboard
Workflows¶
As a user, you can authenticate to OpenFaaS using Open ID Connect with the registered OIDC provider.
- Using
faas-cli pro auth - Using the OpenFaaS Pro Dashboard
The registered OIDC provider can also be used for machine to machine access:
- A client ID and client secret can be used with
faas-cli pro auth
Web Identity Federation support:
- Kubernetes has a built-in OIDC provider, and can be added as a trusted source
- Any accessible OIDC provider such as GitLab, GitHub Actions, Auth0, Okta, Keycloak, can be added as a trusted source
Workflow for human users:
- If a human user is authenticating, then the registered OIDC provider will be used to obtain an id_token.
- This token is then exchanged for an OpenFaaS Access token using the OpenFaaS Gateway.
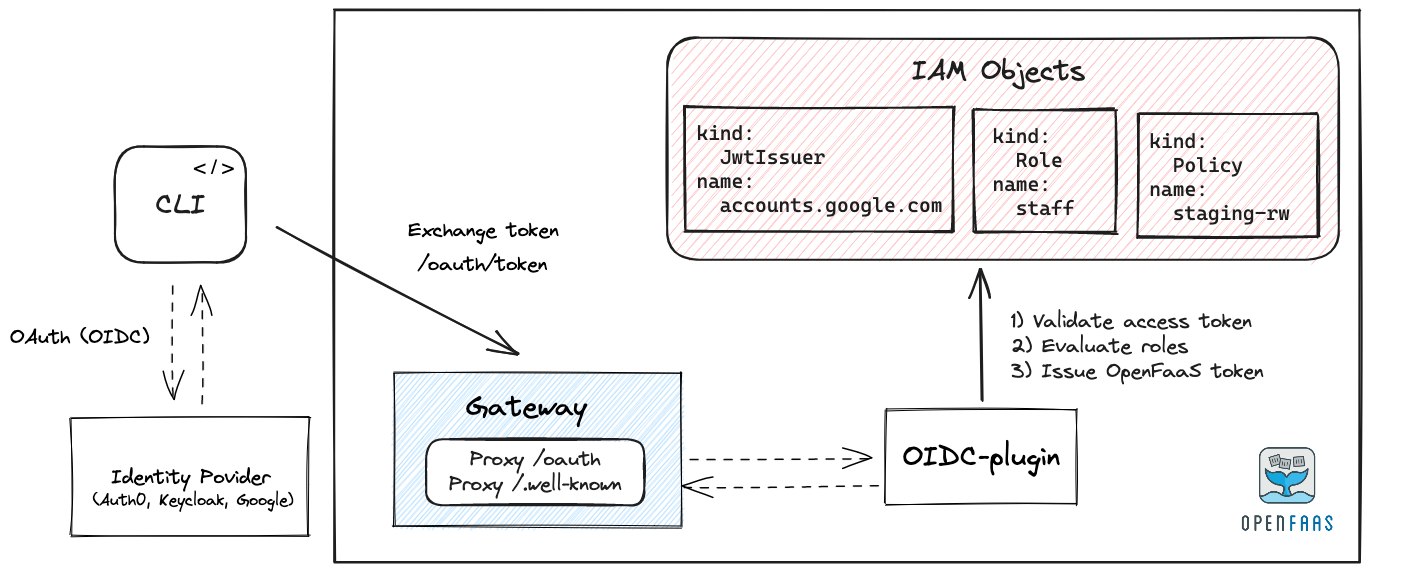
Authentication flow for the OpenFaaS CLI
Workflow for machine users:
- If a machine user is authenticating, then an id_token is usually already present.
- It will be exchanged for an OpenFaaS Access token using the OpenFaaS Gateway.
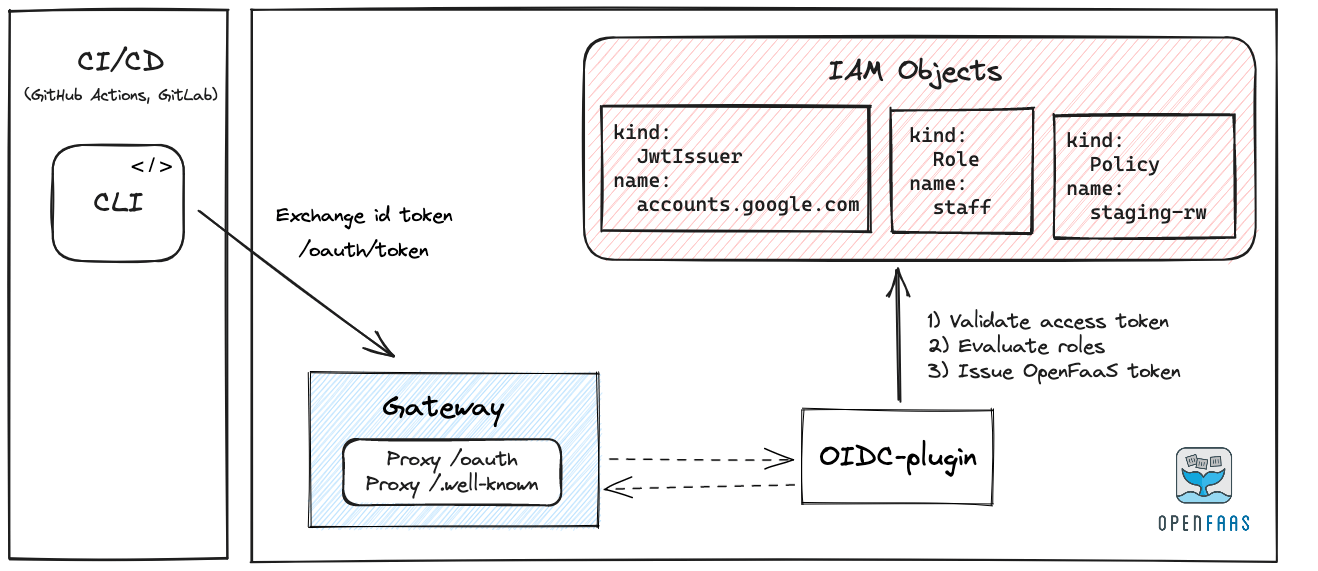
Authentication flow with Identity Federation
There must be at least one registered OIDC provider for human users to authenticate, and then any number of additional issuers can be defined for Web Identity Federation.
Permissions¶
Functions
| Action | Description | Resource scope | Access level |
|---|---|---|---|
Function:Get |
Get the status of functions | cluster, namespace |
Read |
Function:Create |
Create functions | cluster, namespace |
Write |
Function:Update |
Update functions | cluster, namespace |
Write |
Function:Delete |
Delete functions | cluster, namespace |
Write |
Function:List |
List functions | cluster, namespace |
List |
Function:Logs |
Get logs for functions | cluster, namespace |
Read |
Function:Scale |
Set the replica count for functions | cluster, namespace |
Write |
Function:Invoke |
Invoke a function | cluster, namespace, function |
Write |
Invoke permissions
All functions can be invoked by default, however if they have Function Authentication enabled the Function:Invoke action is required to invoke a function.
Secrets
| Action | Description | Resource scope | Access level |
|---|---|---|---|
Secret:List |
List secrets | cluster, namespace |
List |
Secret:Create |
Create secrets | cluster, namespace |
Write |
Secret:Update |
Update secrets | cluster, namespace |
Write |
Secret:Delete |
Delete secrets | cluster, namespace |
Writer |
Namespaces
| Action | Description | Resource scope | Access level |
|---|---|---|---|
Namespace:List |
List function namespaces | cluster, namespace |
List |
Namespace:Get |
Get details of function namespace | cluster, namespace |
Read |
Namespace:Create |
Create function namespaces | cluster, namespace |
Write |
Namespace:Update |
Update function namespaces | cluster, namespace |
Write |
Namespace:Delete |
Delete function namespaces | cluster, namespace |
Write |
System
| Action | Description | Resource scope | Access level |
|---|---|---|---|
System:Info |
Get system provider information | cluster |
Read |
Wildcards can be used to get multiple actions:
Function:*- gives all available function permissions includingFunction:Invoke*- gives all permissions for namespaces, functions, function invocations, secrets etc
Resource scope:
Actions can be scoped cluster wide, or to a specific namespace or function. The supported scope depends on the action to which it is applied.
*- apply actions cluster widestaging:*- apply actions to thestagingnamespacedev:env- apply actions to theenvfunction in thedevnamespace
OpenFaaS IAM language¶
The OpenFaaS IAM language is inspired by AWS IAM, however only a subset of the language is implemented at present.
Note: you can use
faas-cli pro auth --pretty --print --no-exchangeto print out the JWT token obtained from your IdP in order to design your policies.
Principal- this field is optional and can only be used to match the subject of the JWT token i.e.jwt:subexactly. An array can be passed with multiple subjects.
Conditions:
StringEquals- match a string exactly this can be used to match an exact email address of a user or an issuerStringLike- match a string with a wildcard - this could be used to match an email domain for instanceForAnyValue:StringEqual- match a value within an array, this can be used to check group membership
Example principal combined with a condition
The principal is used to match the identifier of the user - which could be anything from a string to a number to a UUID, to an email address.
spec:
policy:
- policy1
principal:
jwt:sub:
- 1234567
- 7654321
condition:
StringEqual:
jwt:iss: ["https://keycloak.example.com/"]
Multiple conditions
When multiple conditions are given they are combined with a logical AND operation.
For example, if you want to match a specific user and anyone with a company email address, you can use:
spec:
policy:
- policy1
condition:
StringEquals:
jwt:iss: "https://keycloak.example.com/realms/openfaas"
StringLike:
jwt:email: "*@example.com"
Multiple context keys within a condition
When multiple context keys are given, they are combined with a logical AND operation. For reference, see the AWS documentation.
For example, if you want to match a specific user and a specific group, you can use:
spec:
policy:
- policy1
condition:
StringEquals:
jwt:iss: "https://keycloak.example.com/realms/openfaas"
jwt:email:
- "webmaster@example.com"
- "devops@example.com"
There is currently no support for negation, such as NotStringEquals or NotStringLike.
Concepts¶
OpenFaaS IAM objects are defined in the openfaas namespace, and need to be created by a system administrator using kubectl, Helm or a GitOps tool.
- JwtIssuer - defines a trusted issuer for OpenFaaS IAM
- Policy - defines a set of permissions and objects on which they can be performed
- Role - defines a set of policies that can be matched to a particular user or identity
Examples¶
Authenticate using Kubernetes JWT tokens¶
You can use Kubernetes Service Account Token Projection to authenticate with the OpenFaaS API. The benefit of these tokens is that they do not need a human to be involved for authorization, so you can use them to automate OpenFaaS without needing to store a password or API key.
Web Identity Federation¶
Web Identity Federation allows you to build a trust relationship with an external identity provider, without sharing long-lived secrets.
OpenFaaS JWT token¶
During authentication an OIDC access token from a trusted IdP is exchanged for an OpenFaaS access token
The faas-cli can be used to get an access token from your IdP and print it out for inspection. This can be useful to see what fields are available when creating Roles.
To print out the decoded OpenFaaS JWT token run:
faas-cli pro auth \
--gateway https://gateway.example.com \
--authority https://keycloak.example.com/realms/openfaas \
--client-id openfaas \
--pretty
Adding the --no-exchange flag stops the CLI from exchanging the access token for an OpenFaaS token. It can be used to print out the original JWT token issued by your IdP for inspection.
Example of a decoded OpenFaaS JWT token:
{
"header": {
"alg": "ES256",
"kid": "ARyHBtoRuXRzCEqR_9NRr_HPP_s36vHKf9_X_Mjpad4x",
"typ": "JWT"
},
"payload": {
"at_hash": "F53gv7injmJ9hUGCOtDgBw",
"aud": "https://gateway.example.com",
"auth_time": 1706088607,
"azp": "openfaas",
"email_verified": true,
"exp": 1706131945,
"family_name": "Verstraete",
"fed:iss": "https://keycloak.example.com/realms/openfaas",
"given_name": "Han",
"groups": [
"openfaas-dev"
],
"iat": 1706088745,
"iss": "https://gateway.example.com",
"jti": "81d42f43-8ebe-4d62-84f8-e1ecab5eb4b1",
"name": "Han Verstraete",
"nonce": "1706088744941521000",
"policy": [
"fn-rw"
],
"preferred_username": "welteki",
"session_state": "65c3df72-dad8-4b2f-95aa-f1556b40ab80",
"sid": "65c3df72-dad8-4b2f-95aa-f1556b40ab80",
"sub": "fed:a81bcb85-72a8-446a-9263-004944a4e9f4",
"typ": "ID"
}
}
The OpenFaaS JWT contains all claims from the original access token and some additional fields.
fed:iss- The federated issuer that issued the original JWT token.policy- The list of policies that are mapped to the access token.
Custom TLS Certificate Authority bundle¶
Add a certificate bundle to OpenFaaS components for use with an internal certificate authority or self signed certificates
Create a secret that contains the CA bundle in the OpenFaaS namespace:
kubectl create secret generic \
-n openfaas \
ca-bundle \
--from-file=ca.crt=ca.crt
Update the OpenFaaS chart and add a reference to the Kubernetes secret with the CA bundle:
caBundleSecretName: ca-bundle
Rotate the signing key¶
The OpenFaaS IAM issuer uses a key to sign OpenFaaS API and Function Invocation JWTs. It is a best practice to rotate signing keys periodically. To rotate the signing key, generate a new key and update the issuer-key secret in the openfaas namespace.
# Generate a key
openssl ecparam -genkey -name prime256v1 -noout -out issuer.key
# Delete the old signing key secret
kubectl delete secret issuer-key
# Recreate the secret with the new key
kubectl -n openfaas \
create secret generic issuer-key \
--from-file=issuer.key=./issuer.key
Restart the OpenFaaS gateway and OIDC plugin:
kubectl rollout restart deploy/oidc-plugin -n openfaas
kubectl rollout restart deploy/gateway -n openfaas
Note
When the signing key is rotated, any OpenFaaS API and Function Invocation JWTs issued with the previous key will be invalidated. Users of the Dashboard and CLI should log out, and re-authenticate.
FAQ¶
-
What Identity Providers are supported?
Any compliant OpenID Connect provider can be used, such as Auth0, Okta, Keycloak, GitLab, GitHub, etc. Some providers have quirks, which may need an additional patch or configuration. Feel free to reach out to us.
-
Which should I use?
If you'd like to get started quickly, and do not have an OIDC solution with your organisation, you can get started with Auth0 on one of their free plans.
-
How can I integrate LDAP users to OpenFaaS IAM?
OpenFaaS IAM is designed to work with any OIDC provider, so you can use any OIDC provider that supports LDAP integration. Examples include Auth0, Azure Active Directory, Okta, Keycloak or Dex.
-
What is the difference between OpenFaaS IAM and Classic OpenFaaS SSO?
OpenFaaS SSO is a stable feature that covers authentication only. It can be made to further restrict authentication to certain users or emails by creating rules within the OIDC provider itself.
OpenFaaS IAM is a complete authentication, authorization and Web Identity Federation solution.
-
What is the difference between OpenFaaS IAM and an admin password?
The default for OpenFaaS CE is to use a single administrative password. It is long lived, and rarely changed, so it's not advisable to share this with your team or to encode it within your CI/CD systems.
OpenFaaS Pro users should use Classic SSO to prevent password sharing and to increase security.
-
Do I need to set up OpenFaaS IAM in development or staging, as well as production?
We recommend using basic authentication in developer environments, and then setting up OpenFaaS IAM in staging and production.
In staging, you could grant broader permissions to your team, and then restrict permissions in production.
-
How do I build a multi-tenant system with OpenFaaS IAM?
There are many considerations, and we'd encourage you to contact the support team to discuss your requirements.
As a guide, for each user or group, create a separate Kubernetes namespace, and then grant them write access to that namespace only.
There are further restrictions that can be applied such as forcing a non-root user for functions, and Kubernetes limit ranges, and a runtimeClass to sandbox the Pod and its containers from accessing the host.
If you're using Google Compute Engine, you can create a node pool with gVisor enabled with a runtimeClass. For Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service, Fargate can be used for isolation using a runtimeClass and node pool.
-
Can we use self-signed certificates or our own private Certificate Authority?
Yes, you can use your own private CA, or self-signed certificates. Create a secret called
ca-bundlein theopenfaasnamespace following the exact instructions in the Helm chart README file, then set thecaBundleSecretName:field in thevalues.yamlfile toca-bundle.